Lecture 10 What is Research
POSITIVISM
 -Facts with a Capital FSeperation of fact from
value (value freedom)
-Facts with a Capital FSeperation of fact from
value (value freedom)-Objectivity
-Measurement rather than argument
-The facts speak for themselves
-Causation
-Separation and control of variables
-Rigorous methodological principles
Approaches to Research
-Empiricism
-Quantitative Research
-Qualitative Research
-Subjectivism
-Quantitative Research
-Qualitative Research
-Subjectivism
Action Research
METHODOLOGY
Method: a way of proceeding about something in
a systematic or logical manner.
Methodology: The science of method, employed in
a particular activity
A logical and predefined and systematic
strategy by which to undertake a research project, including methods of evaluation,
schedules and stated intentions.
SOME METHODOLOGIES
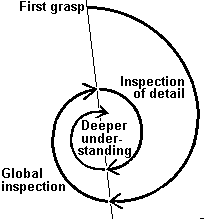 HISTORICAL, SOCIOLOGICAL, SEMIOTIC, COMMUNICATION THEORY, POSTCOLONIAL, PSYCHOANALYSIS , POSTMODERNIST, DISCOURSE ANALYSIS, MARXISM, FEMINISM, QUEER THEORY, GENDER STUDIES, REFLECTIVE PRACTICE, EMPIRICAL INVESTIGATION, HERMENEUTICS, DATA COLLECTION, PARTICIPANT OBSERVATION THE HERMENEUTIC
CIRCLE
HISTORICAL, SOCIOLOGICAL, SEMIOTIC, COMMUNICATION THEORY, POSTCOLONIAL, PSYCHOANALYSIS , POSTMODERNIST, DISCOURSE ANALYSIS, MARXISM, FEMINISM, QUEER THEORY, GENDER STUDIES, REFLECTIVE PRACTICE, EMPIRICAL INVESTIGATION, HERMENEUTICS, DATA COLLECTION, PARTICIPANT OBSERVATION THE HERMENEUTIC
CIRCLE
Developed by Heidegger
Interpretation is a process designed to clarify
an experience and assign meaning to it
This is aided by the hermeneutic circle which involves
looking at different perspectives on events and relating individual components
No comments:
Post a Comment